
Cremation was a common funeral practice in ancient Rome, especially during the Republic and early Empire periods.
The process of cremation involved burning the body of the deceased on a pyre until only ashes remained.
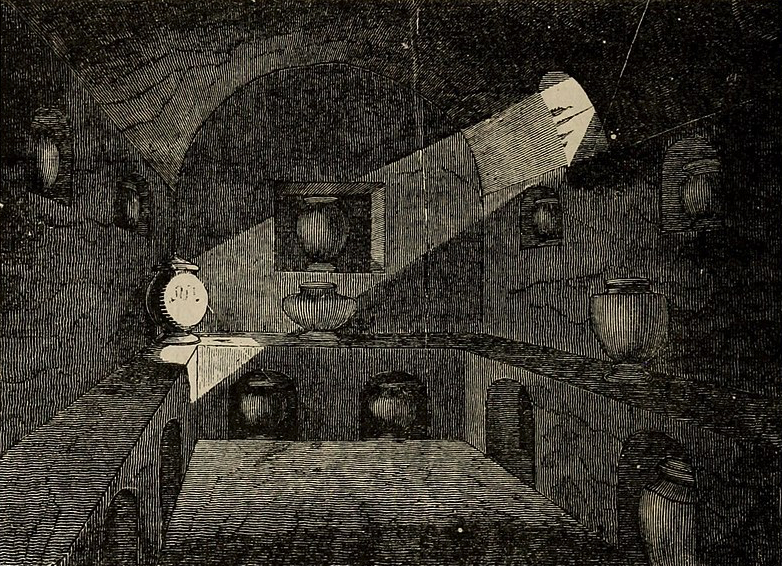
In Roman society, cremation was seen as a practical and economical way to dispose of the dead. The ashes were then placed in an urn and often buried in a tomb or columbarium, which was a structure used for the storage of urns containing ashes.
Some wealthier families built elaborate tombs or mausoleums for the placement of their loved ones’ ashes.

The process of cremation also had a spiritual significance in ancient Rome. It was believed that the act of burning the body symbolized the release of the soul from the physical body and its journey to the afterlife.
The use of fire in the cremation process was also thought to purify the soul and protect it from evil spirits.

Cremation was not the only method of disposing of the dead in ancient Rome, but it was a popular choice among the middle and lower classes.
The rich and powerful often chose to be buried in elaborate tombs or mausoleums, while the poor were often buried in mass graves or simply left to decay.

